Access Answers of Maths NCERT Class 9 Chapter 15 – Probability
Exercise 15.1 Page: 283
Q1. In a cricket match, a batswoman hits a boundary 6 times out of 30 balls she plays. Find the probability that she did not hit a boundary.
Sol: According to the question,
Total number of balls = 30
Numbers of boundary = 6
Number of time batswoman didn’t hit boundary = 30 – 6 = 24
Probability she did not hit a boundary =2430 = 1=45
Total number of balls = 30
Numbers of boundary = 6
Number of time batswoman didn’t hit boundary = 30 – 6 = 24
Probability she did not hit a boundary =
Q2. 1500 families with 2 children were selected randomly, and the following data were recorded:
| Number of girls in a family | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Number of families | 475 | 814 | 211 |
Compute the probability of a family, chosen at random, having
(i) 2 girls (ii) 1 girl (iii) No girl
Also check whether the sum of these probabilities is 1.

(i) 2 girls (ii) 1 girl (iii) No girl
Also check whether the sum of these probabilities is 1.

Q3. Refer to Example 5, Section 14.4, Chapter 14. Find the probability that a student of the class was born in August.
Solution:
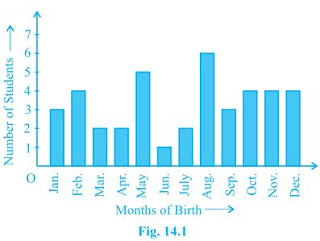
Solution:

Total numbers of students in the class = 40
Numbers of students born in August = 6
The probability that a student of the class was born in August, =640 = 320
Numbers of students born in August = 6
The probability that a student of the class was born in August, =
Q4. Three coins are tossed simultaneously 200 times with the following frequencies of different outcomes:
| Outcome | 3 heads | 2 heads | 1 head | No head |
| Frequency | 23 | 72 | 77 | 28 |
If the three coins are simultaneously tossed again, compute the probability of 2 heads coming up.
Sol: Number of times 2 heads come up = 72
Total number of times the coins were tossed = 200
the probability of 2 heads coming up =72200 = 925
Total number of times the coins were tossed = 200
the probability of 2 heads coming up =
Q5. An organisation selected 2400 families at random and surveyed them to determine a relationship between income level and the number of vehicles in a family. The information gathered is listed in the table below:
| Monthly income (in ₹) | Vehicles per family | |||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | Above 2 | |
| Less than 7000 | 10 | 160 | 25 | 0 |
| 7000-10000 | 0 | 305 | 27 | 2 |
| 10000-13000 | 1 | 535 | 29 | 1 |
| 13000-16000 | 2 | 469 | 59 | 25 |
| 16000 or more | 1 | 579 | 82 | 88 |
Suppose a family is chosen. Find the probability that the family chosen is
Q earning ₹10000 – 13000 per month and owning exactly 2 vehicles.
Q earning ₹10000 – 13000 per month and owning exactly 2 vehicles.
- earning ₹16000 or more per month and owning exactly 1 vehicle.
- earning less than ₹7000 per month and does not own any vehicle.
- earning ₹13000 – 16000 per month and owning more than 2 vehicles.
- owning not more than 1 vehicle.
Sol: Total number of families = 2400
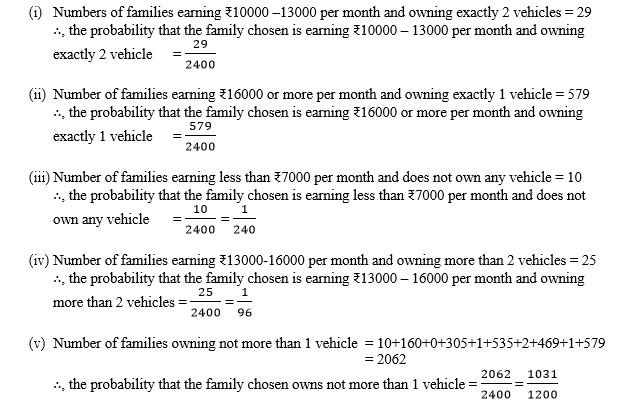

Q6. Refer to Table 14.7, Chapter 14.
(i) Find the probability that a student obtained less than 20% in the mathematics test.
(ii) Find the probability that a student obtained marks 60 or above.Solution:
(i) Find the probability that a student obtained less than 20% in the mathematics test.
(ii) Find the probability that a student obtained marks 60 or above.Solution:
| Marks | Number of students |
| 0 – 20 | 7 |
| 20 – 30 | 10 |
| 30 – 40 | 10 |
| 40 – 50 | 20 |
| 50 – 60 | 20 |
| 60 – 70 | 15 |
| 70 – above | 8 |
| Total | 90 |
Total number of students = 90
(i) Number of students who obtained less than 20% in the mathematics test = 7
the probability that a student obtained less than 20% in the mathematics test =790
the probability that a student obtained less than 20% in the mathematics test =
(ii) Number of students who obtained marks 60 or above = 15+8 = 23 the probability that a student obtained marks 60 or above =23/90
7. To know the opinion of the students about the subject statistics, a survey of 200 students was conducted. The data is recorded in the following table.
| Opinion | Number of students |
| like | 135 |
| dislike | 65 |
Find the probability that a student chosen at random (i) likes statistics, (ii) does not like it.
Sol: Total number of students = 135 + 65 = 200
(i) Number of students who like statistics = 135
the probability that a student likes statistics =135200 = 2740
(i) Number of students who like statistics = 135
the probability that a student likes statistics =
(ii) Number of students who do not like statistics = 65
the probability that a student does not like statistics = 65/200 =1340
the probability that a student does not like statistics = 65/200 =
Q8. Refer to Q.2, Exercise 14.2. What is the empirical probability that an engineer lives:
(i) less than 7 km from her place of work?
(ii) more than or equal to 7 km from her place of work?
(iii) within km from her place of work?
(i) less than 7 km from her place of work?
(ii) more than or equal to 7 km from her place of work?
(iii) within km from her place of work?
Sol: The distance (in km) of 40 engineers from their residence to their place of work were found as follows:
5 3 10 20 25 11 13 7 12 31 19 10 12 17 18 11 3 2 17 16 2 7 9 7 8 3 5 12 15 18 3 12 14 2 9 6 15 15 7 6 12
5 3 10 20 25 11 13 7 12 31 19 10 12 17 18 11 3 2 17 16 2 7 9 7 8 3 5 12 15 18 3 12 14 2 9 6 15 15 7 6 12
Total numbers of engineers = 40
(i) Number of engineers living less than 7 km from their place of work = 9
the probability that an engineer lives less than 7 km from her place of work =9/40
(i) Number of engineers living less than 7 km from their place of work = 9
the probability that an engineer lives less than 7 km from her place of work =9/40
(ii) Number of engineers living more than or equal to 7 km from their place of work
= 40 – 9 = 31
= 40 – 9 = 31
probability that an engineer lives more than or equal to 7 km from her place of work
=3140
=
(iii) Number of engineers living within 12 km from their place of work = 0
the probability that an engineer lives within 1/2km from her place of work = 0/40
= 0
the probability that an engineer lives within 1/2km from her place of work = 0/40
= 0
Q9. Activity : Note the frequency of two-wheelers, three-wheelers and four-wheelers going past during a time interval, in front of your school gate. Find the probability that any one vehicle out of the total vehicles you have observed is a two-wheeler.
Sol: The question is an activity to be performed by the students. Hence, perform the activity by yourself and note down your inference.
Sol: The question is an activity to be performed by the students. Hence, perform the activity by yourself and note down your inference.
Q10. Activity : Ask all the students in your class to write a 3-digit number. Choose any student from the room at random. What is the probability that the number written by her/him is divisible by 3? Remember that a number is divisible by 3, if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
Sol: The question is an activity to be performed by the students. Hence, perform the activity by yourself and note down your inference.
Sol: The question is an activity to be performed by the students. Hence, perform the activity by yourself and note down your inference.
Q11. Eleven bags of wheat flour, each marked 5 kg, actually contained the following weights of flour (in kg):
4.97 5.05 5.08 5.03 5.00 5.06 5.08 4.98 5.04 5.07 5.00
Find the probability that any of these bags chosen at random contains more than 5 kg of flour.
Sol: Total number of bags present = 11
Number of bags containing more than 5 kg of flour = 7
the probability that any of the bags chosen at random contains more than 5 kg of flour
=711
4.97 5.05 5.08 5.03 5.00 5.06 5.08 4.98 5.04 5.07 5.00
Find the probability that any of these bags chosen at random contains more than 5 kg of flour.
Sol: Total number of bags present = 11
Number of bags containing more than 5 kg of flour = 7
the probability that any of the bags chosen at random contains more than 5 kg of flour
=
Q12. In Q.5, Exercise 14.2, you were asked to prepare a frequency distribution table, regarding the concentration of sulphur dioxide in the air in parts per million of a certain city for 30 days. Using this table, find the probability of the concentration of sulphur dioxide in the interval 0.12-0.16 on any of these days.
The data obtained for 30 days is as follows:
0.03 0.08 0.08 0.09 0.04 0.17 0.16 0.05 0.02 0.06 0.18 0.20 0.11 0.08 0.12 0.13 0.22 0.07 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.06 0.09 0.18 0.11 0.07 0.05 0.07 0.01 0.04
Sol: Total number of days in which the data was recorded = 30 days Numbers of days in which sulphur dioxide was present in between the interval 0.12-0.16 = 2 the probability of the concentration of sulphur dioxide in the interval 0.12-0.16 on any of these days =230 = 115
The data obtained for 30 days is as follows:
0.03 0.08 0.08 0.09 0.04 0.17 0.16 0.05 0.02 0.06 0.18 0.20 0.11 0.08 0.12 0.13 0.22 0.07 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.06 0.09 0.18 0.11 0.07 0.05 0.07 0.01 0.04
Sol: Total number of days in which the data was recorded = 30 days Numbers of days in which sulphur dioxide was present in between the interval 0.12-0.16 = 2 the probability of the concentration of sulphur dioxide in the interval 0.12-0.16 on any of these days =
Q13. In Q.1, Exercise 14.2, you were asked to prepare a frequency distribution table regarding the blood groups of 30 students of a class. Use this table to determine the probability that a student of this class, selected at random, has blood group AB.
The blood groups of 30 students of Class VIII are recorded as follows:
A, B, O, O, AB, O, A, O, B, A, O, B, A, O, O, A, AB, O, A, A, O, O, AB, B, A, O, B, A, B, O.
The blood groups of 30 students of Class VIII are recorded as follows:
A, B, O, O, AB, O, A, O, B, A, O, B, A, O, O, A, AB, O, A, A, O, O, AB, B, A, O, B, A, B, O.
Sol: Total numbers of students = 30 Number of students having blood group AB = 3 the probability that a student of this class, selected at random, has blood group AB = 330 = 110
Comments
Post a Comment