Access Answers of Maths NCERT Class 9 Chapter 7 – Triangles
Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise: 7.1 (Page No: 118)
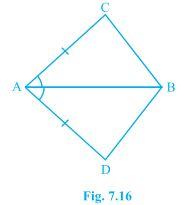
1. In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB bisect ∠A (see Fig. 7.16). Show that ΔABC ≅ ΔABD. What can you say about BC and BD?
Solution:
It is given that AC and AD are equal i.e. AC=AD and the line segment AB bisects ∠A.
We will have to now prove that the two triangles ABC and ABD are similar i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔABD
Proof:
Consider the triangles ΔABC and ΔABD,
(i) AC = AD (It is given in the question)
(ii) AB = AB (Common)
(iii) ∠CAB = ∠DAB (Since AB is the bisector of angle A)
So, by SAS congruency criterion, ΔABC ≅ ΔABD.
For the 2nd part of the question, BC and BD are of equal lengths.
(Page No: 119)
2. ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC and ∠DAB = ∠CBA (see Fig. 7.17). Prove that
(i) ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
(ii) BD = AC
(iii) ∠ABD = ∠BAC.
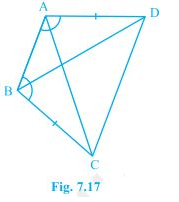
Solution:
The given parameters from the questions are ∠DAB = ∠CBA and AD = BC.
(i) ΔABD and ΔBAC are similar by SAS congruency as
AB = BA (It is the common arm)
∠DAB = ∠CBA and AD = BC (These are given in the question)
So, triangles ABD and BAC are similar i.e. ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC. (Hence proved).
(ii) It is now known that ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC so,
BD = AC (by the rule of CPCT).
(iii) Since ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC so,
Angles ∠ABD = ∠BAC (by the rule of CPCT).
3. AD and BC are equal perpendiculars to a line segment AB (see Fig. 7.18). Show that CD bisects AB.
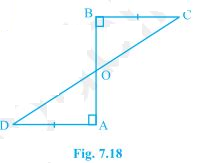
Solution:
It is given that AD and BC are two equal perpendiculars to AB.
We will have to prove that CD is the bisector of AB
Proof:
Triangles ΔAOD and ΔBOC are similar by AAS congruency since:
(i) ∠A = ∠B (They are perpendiculars)
(ii) AD = BC (As given in the question)
(iii) ∠AOD = ∠BOC (They are vertically opposite angles)
∴ ΔAOD ≅ ΔBOC.
So, AO = OB ( by the rule of CPCT).
Thus, CD bisects AB (Hence proved).
4. l and m are two parallel lines intersected by another pair of parallel lines p and q (see Fig. 7.19). Show that ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA.
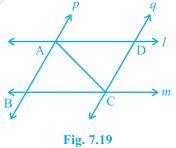
Solution:
It is given that p ∥ q and l ∥ m
To prove:
Triangles ABC and CDA are similar i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA
Proof:
Consider the ΔABC and ΔCDA,
(i) ∠BCA = ∠DAC and ∠BAC = ∠DCA Since they are alternate interior angles
(ii) AC = CA as it is the common arm
So, by ASA congruency criterion ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA.
5. Line l is the bisector of an angle ∠A and B is any point on l. BP and BQ are perpendiculars from B to the arms of ∠A (see Fig. 7.20). Show that:
(i) ΔAPB ≅ ΔAQB
(ii) BP = BQ or B is equidistant from the arms of ∠A.
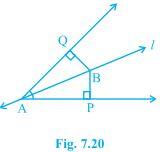
Solution:
It is given that the line “l” is the bisector of angle ∠A and the line segments BP and BQ are perpendiculars drawn from l.
(i) ΔAPB and ΔAQB are similar by AAS congruency because:
∠P = ∠Q (They are the two right angles)
AB = AB (It is the common arm)
∠BAP = ∠BAQ (As line l is the bisector of angle A)
So, ΔAPB ≅ ΔAQB.
(ii) By the rule of CPCT, BP = BQ. So, it can be said the point B is equidistant from the arms of ∠A.
(Page No: 120)
6. In Fig. 7.21, AC = AE, AB = AD and ∠BAD = ∠EAC. Show that BC = DE.
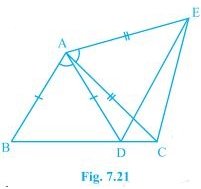
Solution:
It is given in the question that AB = AD, AC = AE, and ∠BAD = ∠EAC
To proof:
The line segment BC and DE are similar i.e. BC = DE
Proof:
We know that ∠BAD = ∠EAC
Now, by adding ∠DAC on both sides we get,
∠BAD + ∠DAC = ∠EAC + ∠DAC
This implies, ∠BAC = ∠EAD
Now, ΔABC and ΔADE are similar by SAS congruency since:
(i) AC = AE (As given in the question)
(ii) ∠BAC = ∠EAD
(iii) AB = AD (It is also given in the question)
∴ Triangles ABC and ADE are similar i.e. ΔABC ≅ ΔADE.
So, by the rule of CPCT, it can be said that BC = DE.
7. AB is a line segment and P is its mid-point. D and E are points on the same side of AB such that ∠BAD = ∠ABE and ∠EPA = ∠DPB (see Fig. 7.22). Show that
(i) ΔDAP ≅ ΔEBP
(ii) AD = BE
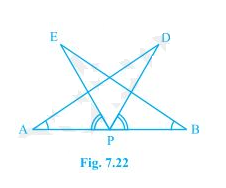
Answer
In the question, it is given that P is the mid-point of line segment AB. Also, ∠BAD = ∠ABE and ∠EPA = ∠DPB
(i) It is given that ∠EPA = ∠DPB
Now, add ∠DPE om both sides,
∠EPA + ∠DPE = ∠DPB + ∠DPE
This implies that angles DPA and EPB are equal i.e. ∠DPA = ∠EPB
Now, consider the triangles DAP and EBP.
∠DPA = ∠EPB
AP = BP (Since P is the mid-point of the line segement AB)
∠BAD = ∠ABE (As given in the question)
So, by ASA congruency, ΔDAP ≅ ΔEBP.
(ii) By the rule of CPCT, AD = BE.
8. In right triangle ABC, right angled at C, M is the mid-point of hypotenuse AB. C is joined to M and produced to a point D such that DM = CM. Point D is joined to point B (see Fig. 7.23). Show that:
(i) ΔAMC ≅ ΔBMD
(ii) ∠DBC is a right angle.
(iii) ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB
(iv) CM = 1/2 AB
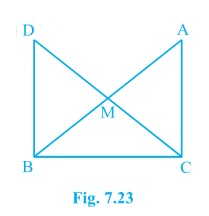
Solution:
It is given that M is the mid-point of the line segment AB, ∠C = 90°, and DM = CM
(i) Consider the triangles ΔAMC and ΔBMD:
AM = BM (Since M is the mid-point)
CM = DM (Given in the question)
∠CMA = ∠DMB (They are vertically opposite angles)
So, by SAS congruency criterion, ΔAMC ≅ ΔBMD.
(ii) ∠ACM = ∠BDM (by CPCT)
∴ AC ∥ BD as alternate interior angles are equal.
Now, ∠ACB + ∠DBC = 180° (Since they are co-interiors angles)
⇒ 90° + ∠B = 180°
∴ ∠DBC = 90°
(iii) In ΔDBC and ΔACB,
BC = CB (Common side)
∠ACB = ∠DBC (They are right angles)
DB = AC (by CPCT)
So, ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB by SAS congruency.
(iv) DC = AB (Since ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB)
⇒ DM = CM = AM = BM (Since M the is mid-point)
So, DM + CM = BM + AM
Hence, CM + CM = AB
⇒ CM = (½) AB
Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise: 7.2 (Page No: 123)
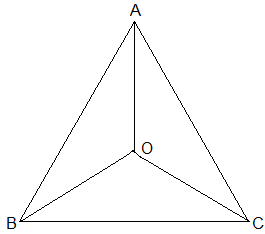
1. In an isosceles triangle ABC, with AB = AC, the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C intersect each other at O. Join A to O. Show that :
(i) OB = OC (ii) AO bisects ∠A
Solution:
Given:
-> AB = AC and
-> the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C intersect each other at O
(i) Since ABC is an isosceles with AB = AC,
=> ∠B = ∠C
⇒ 1/2∠B = 1/2∠C
⇒ ∠OBC = ∠OCB (Angle bisectors)
∴ OB = OC (Side opposite to the equal angles are equal.)
(ii) In ΔAOB and ΔAOC,
AB = AC (Given in the question)
AO = AO (Common arm)
OB = OC (As Proved Already)
So, ΔAOB ≅ ΔAOC by SSS congruence condition.
∠BAO = ∠CAO (by CPCT)
Thus, AO bisects ∠A.
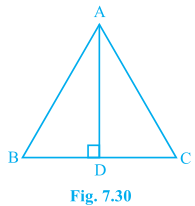
2. In ΔABC, AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC (see Fig. 7.30). Show that ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC.
Solution:
It is given that AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC
To prove:
AB = AC
Proof:
In ΔADB and ΔADC,
AD = AD (It is the Common arm)
∠ADB = ∠ADC
BD = CD (Since AD is the perpendicular bisector)
So, ΔADB ≅ ΔADC by SAS congruency criterion.
AB = AC (by CPCT)
(Page No: 124)
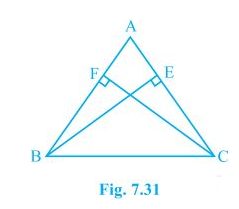
3. ABC is an isosceles triangle in which altitudes BE and CF are drawn to equal sides AC and AB respectively (see Fig. 7.31). Show that these altitudes are equal.
Solution:
Given:
(i) BE and CF are altitudes.
(ii) AC = AB
To prove:
BE = CF
Proof:
Triangles ΔAEB and ΔAFC are similar by AAS congruency since
∠A = ∠A (It is the common arm)
∠AEB = ∠AFC (They are right angles)
AB = AC (Given in the question)
∴ ΔAEB ≅ ΔAFC and so, BE = CF (by CPCT).
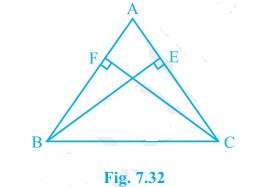
4. ABC is a triangle in which altitudes BE and CF to sides AC and AB are equal (see Fig. 7.32). Show that
(i) ΔABE ≅ ΔACF
(ii) AB = AC, i.e., ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Solution:
It is given that BE = CF
(i) In ΔABE and ΔACF,
∠A = ∠A (It is the common angle)
∠AEB = ∠AFC (They are right angles)
BE = CF (Given in the question)
∴ ΔABE ≅ ΔACF by AAS congruency condition.
(ii) AB = AC by CPCT and so, ABC is an isosceles triangle.
5. ABC and DBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC (see Fig. 7.33). Show that ∠ABD = ∠ACD.
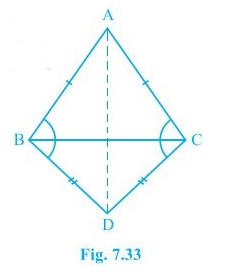
Solution:
In the question, it is given that ABC and DBC are two isosceles triangles.
We will have to show that ∠ABD = ∠ACD
Proof:
Triangles ΔABD and ΔACD are similar by SSS congruency since
AD = AD (It is the common arm)
AB = AC (Since ABC is an isosceles triangle)
BD = CD (Since BCD is an isosceles triangle)
So, ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.
∴ ∠ABD = ∠ACD by CPCT.
6. ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. Side BA is produced to D such that AD = AB (see Fig. 7.34). Show that ∠BCD is a right angle.
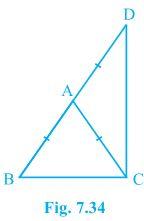
Solution:
It is given that AB = AC and AD = AB
We will have to now prove ∠BCD is a right angle.
Proof:
Consider ΔABC,
AB = AC (It is given in the question)
Also, ∠ACB = ∠ABC (They are angles opposite to the equal sides and so, they are equal)
Now, consider ΔACD,
AD = AB
Also, ∠ADC = ∠ACD (They are angles opposite to the equal sides and so, they are equal)
Now,
In ΔABC,
∠CAB + ∠ACB + ∠ABC = 180°
So, ∠CAB + 2∠ACB = 180°
⇒ ∠CAB = 180° – 2∠ACB — (i)
Similarly in ΔADC,
∠CAD = 180° – 2∠ACD — (ii)
also,
∠CAB + ∠CAD = 180° (BD is a straight line.)
Adding (i) and (ii) we get,
∠CAB + ∠CAD = 180° – 2∠ACB + 180° – 2∠ACD
⇒ 180° = 360° – 2∠ACB – 2∠ACD
⇒ 2(∠ACB + ∠ACD) = 180°
⇒ ∠BCD = 90°
7. ABC is a right-angled triangle in which ∠A = 90° and AB = AC. Find ∠B and ∠C.
Solution:
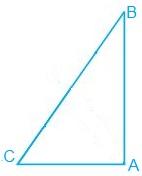
In the question, it si given that
∠A = 90° and AB = AC
AB = AC
⇒ ∠B = ∠C (They are angles opposite to the equal sides and so, they are equal)
Now,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° (Since the sum of the interior angles of the triangle)
∴ 90° + 2∠B = 180°
⇒ 2∠B = 90°
⇒ ∠B = 45°
So, ∠B = ∠C = 45°
8. Show that the angles of an equilateral triangle are 60° each.
Solution:
Let ABC be an equilateral triangle as shown below:
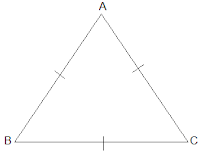
Here, BC = AC = AB (Since the length of all sides is same)
⇒ ∠A = ∠B = ∠C (Sides opposite to the equal angles are equal.)
Also, we know that
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
⇒ 3∠A = 180°
⇒ ∠A = 60°
∴ ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°
So, the angles of an equilateral triangle are always 60° each.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise: 7.3 (Page No: 128)
1. ΔABC and ΔDBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC and vertices A and D are on the same side of BC (see Fig. 7.39). If AD is extended to intersect BC at P, show that
(i) ΔABD ≅ ΔACD
(ii) ΔABP ≅ ΔACP
(iii) AP bisects ∠A as well as ∠D.
(iv) AP is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
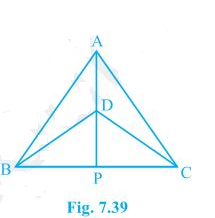
Solution:
In the above question, it is given that ΔABC and ΔDBC are two isosceles triangles.
(i) ΔABD and ΔACD are similar by SSS congruency because:
AD = AD (It is the common arm)
AB = AC (Since ΔABC is isosceles)
BD = CD (Since ΔDBC is isosceles)
∴ ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.
(ii) ΔABP and ΔACP are similar as:
AP = AP (It is the common side)
∠PAB = ∠PAC ( by CPCT since ΔABD ≅ ΔACD)
AB = AC (Since ΔABC is isosceles)
So, ΔABP ≅ ΔACP by SAS congruency condition.
(iii) ∠PAB = ∠PAC by CPCT as ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.
AP bisects ∠A. — (i)
Also, ΔBPD and ΔCPD are similar by SSS congruency as
PD = PD (It is the common side)
BD = CD (Since ΔDBC is isosceles.)
BP = CP (by CPCT as ΔABP ≅ ΔACP)
So, ΔBPD ≅ ΔCPD.
Thus, ∠BDP = ∠CDP by CPCT. — (ii)
Now by comparing (i) and (ii) it can be said that AP bisects ∠A as well as ∠D.
(iv) ∠BPD = ∠CPD (by CPCT as ΔBPD ≅ ΔCPD)
and BP = CP — (i)
also,
∠BPD + ∠CPD = 180° (Since BC is a straight line.)
⇒ 2∠BPD = 180°
⇒ ∠BPD = 90° —(ii)
Now, from equations (i) and (ii), it can be said that
AP is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
2. AD is an altitude of an isosceles triangle ABC in which AB = AC. Show that
(i) AD bisects BC (ii) AD bisects ∠A.
Solution:
It is given that AD is an altitude and AB = AC. The diagram is as follows:
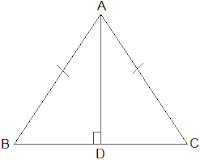
(i) In ΔABD and ΔACD,
∠ADB = ∠ADC = 90°
AB = AC (It is given in the question)
AD = AD (Common arm)
∴ ΔABD ≅ ΔACD by RHS congruence condition.
Now, by the rule of CPCT,
BD = CD.
So, AD bisects BC
(ii) Again by the rule of CPCT, ∠BAD = ∠CAD
Hence, AD bisects ∠A.
3. Two sides AB and BC and median AM of one triangle ABC are respectively equal to sides PQ and QR and median PN of ΔPQR (see Fig. 7.40). Show that:
(i) ΔABM ≅ ΔPQN
(ii) ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
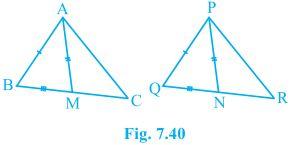
Solution:
Given parameters are:
AB = PQ,
BC = QR and
AM = PN
(i) 1/2 BC = BM and 1/2QR = QN (Since AM and PN are medians)
Also, BC = QR
So, 1/2 BC = 1/2QR
⇒ BM = QN
In ΔABM and ΔPQN,
AM = PN and AB = PQ (As given in the question)
BM = QN (Already proved)
∴ ΔABM ≅ ΔPQN by SSS congruency.
(ii) In ΔABC and ΔPQR,
AB = PQ and BC = QR (As given in the question)
∠ABC = ∠PQR (by CPCT)
So, ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR by SAS congruency.
4. BE and CF are two equal altitudes of a triangle ABC. Using RHS congruence rule, prove that the triangle ABC is isosceles.
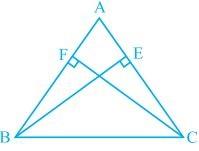 .
.
Solution:
It is known that BE and CF are two equal altitudes.
Now, in ΔBEC and ΔCFB,
∠BEC = ∠CFB = 90° (Same Altitudes)
BC = CB (Common side)
BE = CF (Common side)
So, ΔBEC ≅ ΔCFB by RHS congruence criterion.
Also, ∠C = ∠B (by CPCT)
Therefore, AB = AC as sides opposite to the equal angles is always equal.
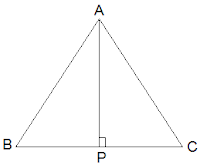
5. ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC. Draw AP ⊥ BC to show that ∠B = ∠C.
Solution:
In the question, it is given that AB = AC
Now, ΔABP and ΔACP are similar by RHS congruency as
∠APB = ∠APC = 90° (AP is altitude)
AB = AC (Given in the question)
AP = AP (Common side)
So, ΔABP ≅ ΔACP.
∴ ∠B = ∠C (by CPCT)
Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Exercise: 7.4 (Page No: 132)
1. Show that in a right angled triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side.
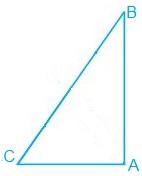
Solution:
It is known that ABC is a triangle right angled at B.
We know that,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
Now, if ∠B + ∠C = 90° then ∠A has to be 90°.
Since A is the largest angle of the triangle, the side opposite to it must be the largest.
So, AB is the hypotenuse which will be the largest side of the above right-angled triangle i.e. ΔABC.
2. In Fig. 7.48, sides AB and AC of ΔABC are extended to points P and Q respectively. Also, ∠PBC < ∠QCB. Show that AC > AB.
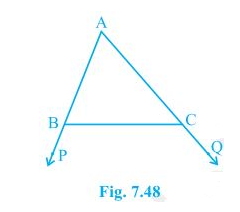
Solution:
It is given that ∠PBC < ∠QCB
We know that ∠ABC + ∠PBC = 180°
So, ∠ABC = 180° – ∠PBC
Also,
∠ACB + ∠QCB = 180°
Therefore ∠ACB = 180° – ∠QCB
Now, since ∠PBC < ∠QCB,
∴ ∠ABC > ∠ACB
Hence, AC > AB as sides opposite to the larger angle is always larger.
3. In Fig. 7.49, ∠B < ∠A and ∠C < ∠D. Show that AD < BC.
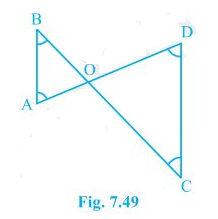
Solution:
In the question, it is mentioned that angles B and angle C is smaller than angles A and D respectively i.e. ∠B < ∠A and ∠C < ∠D
Now,
Since the side opposite to the smaller angle is always smaller
AO < BO — (i)
And OD < OC —(ii)
By adding equation (i) and equation (ii) we get
AO + OD < BO + OC
So, AD < BC
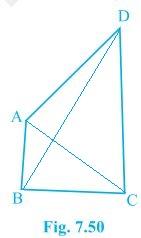
4. AB and CD are respectively the smallest and longest sides of a quadrilateral ABCD (see Fig. 7.50).
Show that ∠A > ∠C and ∠B > ∠D.
Solution:
In ΔABD,
AB < AD < BD
So, ∠ADB < ∠ABD — (i) (Since angle opposite to longer side is always larger)
Now, in ΔBCD,
BC < DC < BD
Hence, it can be concluded that
∠BDC < ∠CBD — (ii)
Now, by adding equation (i) and equation (ii) we get,
∠ADB + ∠BDC < ∠ABD + ∠CBD
=> ∠ADC < ∠ABC
=> ∠B > ∠D
Similarly, In triangle ABC,
∠ACB < ∠BAC — (iii) (Since the angle opposite to the longer side is always larger)
Now, In ΔADC,
∠DCA < ∠DAC — (iv)
By adding equation (iii) and equation (iv) we get,
∠ACB + ∠DCA < ∠BAC + ∠DAC
⇒ ∠BCD < ∠BAD
∴ ∠A > ∠C
5. In Fig 7.51, PR > PQ and PS bisect ∠QPR. Prove that ∠PSR > ∠PSQ.
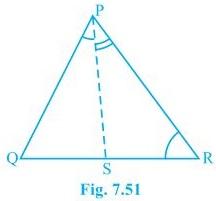
Solution:
It is given that PR > PQ and PS bisects ∠QPR
Now we will have to prove that angle PSR is smaller than PSQ i.e. ∠PSR > ∠PSQ
Proof:
∠QPS = ∠RPS — (ii) (As PS bisects ∠QPR)
∠PQR > ∠PRQ — (i) (Since PR > PQ as angle opposite to the larger side is always larger)
∠PSR = ∠PQR + ∠QPS — (iii) (Since the exterior angle of a triangle equals to the sum of opposite interior angles)
∠PSQ = ∠PRQ + ∠RPS — (iv) (As the exterior angle of a triangle equals to the sum of opposite interior angles)
By adding (i) and (ii)
∠PQR + ∠QPS > ∠PRQ + ∠RPS
Now, from (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get
∠PSR > ∠PSQ
(Page No: 133)
6. Show that of all line segments drawn from a given point not on it, the perpendicular line segment is the shortest.
Solution:
First, let “l” be a line segment and “B” be a point lying on it. A line AB perpendicular to l is now drawn. Also, let C be any other point on l. The diagram will be as follows:
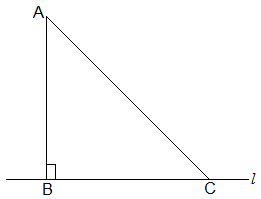
To prove:
AB < AC
Proof:
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°
Now, we know that
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
∴ ∠A + ∠C = 90°
Hence, ∠C must be an acute angle which implies ∠C < ∠B
So, AB < AC (As the side opposite to the larger angle is always larger)
Comments
Post a Comment